A dog senses a nearby stranger and gives a protective bark. A haughty cat slinks by, ignoring everyone. A cow chews its cud and moos in contentment. At least, that’s how we may interpret their actions. We take our own experiences to understand and relate to the animals around us — using our imagination to fill in any gaps along the way. But such assumptions are often wrong. Scientists who study animal behavior and welfare are coming to understand how many creatures experience the world. Researchers are getting insight into a wide range of animals, from mice to octopuses, and are finding that many species can feel emotions similar to those of humans. Knowing all this could begin to change how we treat animals, as studying what animals feel and experience is a challenge due to the personal nature of emotions.
Key Takeaways
- Scientists are studying the emotional intelligence of a wide range of animals, from mice to octopuses.
- Many species can experience emotions similar to those of humans, challenging long-held assumptions.
- Understanding the emotional lives of animals could change how we treat them, as emotions are deeply personal.
- Studying pet emotions and behavior provides valuable insights into the human-animal bond.
- Recognizing the emotional complexity of pets is crucial for their overall well-being.
Introduction to the Emotional World of Pets
In the past, researchers believed it was impossible to understand the inner emotional lives of animals. However, that perspective has undergone a profound shift in recent decades. Biologist Charles Darwin proposed in 1872 that many species could have evolved emotions, suggesting that features like fear are present in almost all animals. This groundbreaking idea laid the foundation for a deeper exploration of the emotional intelligence in animals and the science of pet emotions.
Uncovering the Complexity of Animal Emotions
The late 20th century saw a surge of researchers, such as Marian Stamp Dawkins, probing the emotional experiences of animals and seeking parallels in how people and other species process their emotions. Scientists are now employing a variety of methods, including studying animal behavior, physiology, and brain activity, to gain unprecedented insights into the emotional lives of a wide range of species, from rats to octopuses.
Challenging Misconceptions about Pet Feelings
This groundbreaking research is challenging long-held assumptions and helping us better understand the complexity of animal emotions. By exploring the neuroethology of companion animals and the evolutionary basis of pet emotions, scientists are uncovering the depth and nuance of how our furry, feathered, and scaly friends experience and communicate their feelings.
The Science Behind Pet Emotions
As the field of animal psychology continues to evolve, researchers have uncovered fascinating insights into the emotional lives of our beloved pets. Through cutting-edge brain studies, scientists are revealing that dogs and other companion animals share a surprisingly similar emotional range to humans, with the ability to experience emotions like joy, fear, love, and even jealousy.
Brain Studies Revealing Emotional Similarities
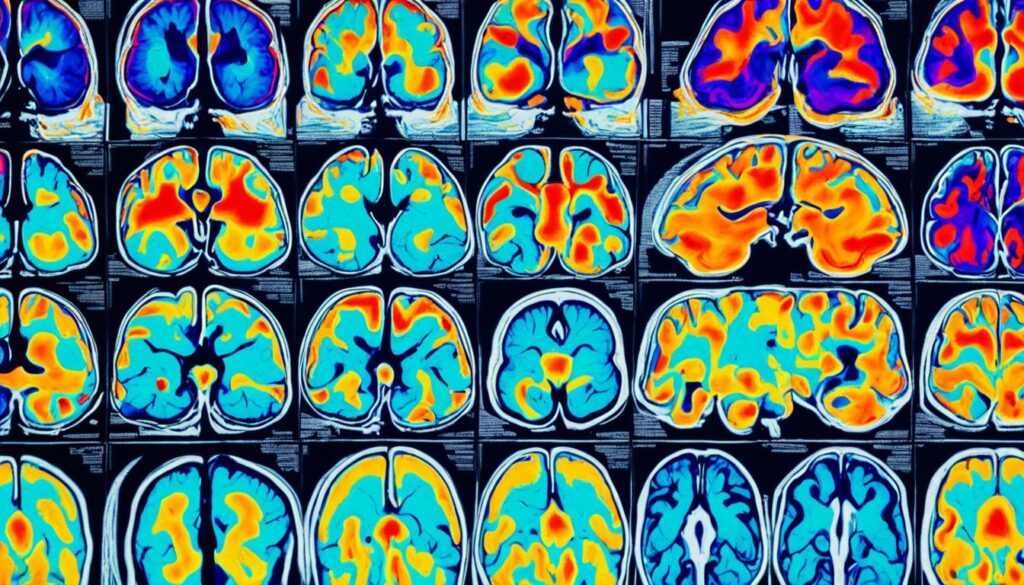
Recent research using advanced imaging techniques has provided a glimpse into the neural activity of our animal friends. Studies on dogs, for instance, have shown that their brains light up in response to positive stimuli, much like our own brains do when we experience happiness or affection. This suggests that our canine companions have the capacity to feel a wide array of emotions, challenging the long-held belief that animals are mere automatons, devoid of complex inner experiences.
Physiological Markers of Animal Emotions
Beyond brain studies, scientists are also utilizing physiological markers to gain a deeper understanding of animal emotions. By monitoring changes in heart rate, hormone levels, and other bodily functions, researchers can glean valuable insights into the emotional states of a diverse range of species, from rats to octopuses. These physical indicators provide an objective window into the subjective experiences of our animal companions, allowing us to better empathize with and cater to their emotional needs.
Evolutionary Perspectives on Emotional Development
From an evolutionary standpoint, the development of emotions in animals is believed to be closely tied to their survival and social needs. Many species, including humans, share a common emotional foundation due to our shared evolutionary history. This suggests that the ability to experience feelings like fear, joy, and attachment has played a crucial role in the adaptation and success of various animal species, underscoring the fundamental importance of emotional intelligence in the natural world.
Recognizing Emotional Signals in Pets
As pet owners, we often strive to understand the emotional states of our furry, feathered, or scaly companions. Decoding the complex language of pet emotions is essential for fostering stronger bonds and providing the best possible care. By observing their body language and behavior cues, as well as interpreting their vocalizations and sounds, we can gain invaluable insights into the emotional intelligence and interspecies communication that make our pets such integral parts of our lives.
Body Language and Behavior Cues
Pets have a rich repertoire of body language and behavior cues that can reveal their emotional states. A wagging tail, purring, or playful antics often signify happiness and contentment, while hiding, flattened ears, or a tucked tail can be indicators of fear or anxiety. Pets also express affection through cuddling, following their owners around, or sitting on their laps. Jealousy can manifest in possessive or acting-out behaviors when the pet’s owner gives attention to another animal or person.
Interpreting Vocalizations and Sounds
In addition to body language, vocalizations and sounds can provide valuable clues about a pet’s emotional state. Barks, meows, or moos can convey a range of emotions, from excitement and playfulness to distress and fear. By decoding pet expressions and reading pet body language, we can gain a deeper understanding of the neuroethology of companion animals and the evolutionary basis of pet emotions.
Mastering the art of understanding pet emotions and interspecies emotional communication is a journey of discovery, one that strengthens the animal-human bond and pet mental health. By tuning in to the subtle cues and signals our pets share with us, we can foster a more meaningful and compassionate relationship that celebrates the emotional intelligence in animals and the science of pet emotions.
The Science of Pet Emotions
The scientific study of pet emotions is a relatively new field, but researchers have made significant progress in understanding the emotional lives of our furry, feathered, and scaly companions. By using various methods, such as behavioral observations, physiological measurements, and brain imaging, scientists are gaining valuable insights into the emotional experiences of a wide range of animal species. This research is challenging long-held assumptions and helping us appreciate the depth and complexity of the emotional world of pets.
Through neuroethological studies, researchers have uncovered remarkable similarities between the brain structures and neurochemical pathways involved in emotion processing in humans and other animals, particularly our beloved pets. For instance, studies on dog brains have revealed that they possess regions responsible for processing positive emotions, such as joy and love, as well as negative emotions, like fear and anxiety.
Physiological markers, such as changes in heart rate, hormone levels, and brain activity, also provide valuable clues about the emotional states of our animal companions. By closely observing and measuring these biological indicators, scientists are gaining a deeper understanding of the emotional intelligence and emotional complexity present in a diverse range of species, from rats to octopuses.
Furthermore, the evolutionary basis of pet emotions has been a subject of intense study, as researchers explore the shared emotional foundations between humans and other animals. This research suggests that the development of emotions in pets is closely tied to their survival and social needs, highlighting the adaptive value of emotional experiences in the natural world.
| Emotional Capacity | Examples in Pets | Relevant Research |
|---|---|---|
| Joy and Affection | Wagging tails, purring, cuddling behaviors | Studies on dog brain activity and feline bonding behaviors |
| Fear and Anxiety | Hiding, trembling, panting, aggressive displays | Physiological measurements of stress hormones and heart rate changes in pets |
| Jealousy and Possessiveness | Attention-seeking, aggression towards other pets or people | Observations of pet behaviors and brain activity during social interactions |
| Grief and Loss | Reduced activity, decreased appetite, vocalization changes | Studies on behavioral changes and hormonal profiles in pets after the loss of a companion |
The scientific exploration of pet emotions is a rapidly evolving field, continuously challenging our preconceptions and deepening our understanding of the emotional capacities of our animal companions. By leveraging the latest advancements in animal behavior research, neuroscience, and evolutionary biology, scientists are unveiling the complexity and diversity of the emotional lives of pets, paving the way for more compassionate and enriching approaches to animal care and the human-animal bond.

Emotional Bonds and Attachments
As a pet owner, I’ve witnessed the profound emotional bonds that can form between humans and their animal companions. The science of pet emotions has shed light on the depth of these connections, revealing that many pets can form deep attachments and experience grief much like we do.
Observing Grief and Loss Behaviors
When a beloved pet or family member passes away, our animal friends often display behaviors that suggest they are grieving the loss. From changes in body language and vocalizations to a clear sense of sadness and withdrawal, these observations highlight the emotional intelligence and sensitivity of our animal psychology and pet behavior analysis.
Witnessing these emotional intelligence in animals can be heartbreaking, but it also underscores the importance of recognizing and understanding pet emotions as we navigate the delicate process of loss and bereavement with our furry, feathered, or scaly loved ones.
The Depth of Human-Animal Connections
Beyond the shared experiences of grief, my research into the neuroethology of companion animals and the evolutionary basis of pet emotions has shown me the profound depth of the human-animal bond. Pets not only decode pet body language and interspecies emotional communication, but they also serve as emotional companions that can provide comfort, support, and a sense of purpose in our lives.
By reading pet expressions and decoding pet expressions, we can better understand pet mental health and nurture the animal-human bond that is so vital to the well-being of both species.
Emotions and Animal Welfare
Recognizing the emotional lives of our animal companions is crucial for ensuring their overall well-being. As we delve deeper into the science of pet emotions, animal psychology, and pet behavior analysis, we gain valuable insights into the emotional intelligence in animals and how to better understand pet emotions, decode pet body language, and foster interspecies emotional communication.
Understanding Stress and Anxiety in Pets
By studying the neuroethology of companion animals and the evolutionary basis of pet emotions, researchers are uncovering the ways in which our pets experience interspecies communication and express their emotions through body language and vocalizations. Recognizing the signs of pet mental health issues, such as stress and anxiety, can help pet owners provide the necessary care and support to maintain the animal-human bond and promote the overall well-being of our furry, feathered, or scaly friends.
Enrichment for Emotional Well-being
Incorporating enrichment activities, like providing toys, varied environments, and opportunities for social interaction, can help promote emotional well-being and reduce negative emotional states in pets. By prioritizing the emotional needs of our animal companions and reading pet body language to understand their needs, we can ensure their overall health and happiness.
The Role of Emotions in Training and Behavior
Emotions play a crucial role in shaping pet behavior and how they respond to training. As someone who deeply cares about the welfare of animals, I’ve come to understand the importance of considering the emotional aspects of training and behavior modification.
Positive Reinforcement and Confidence Building
Positive reinforcement training, which rewards desirable behaviors, can be an incredibly effective way to build a pet’s confidence and strengthen the bond between the animal and their caretaker. By focusing on positive emotions and reinforcing the behaviors we want to see, we can encourage our pets to engage more willingly and enthusiastically in the training process. This not only leads to better learning outcomes but also helps foster a sense of trust and security within the animal-human relationship.
Addressing Emotional Triggers and Fears
Understanding a pet’s emotional triggers and fears is also essential for improving their behavior and overall well-being. By addressing these emotional factors through gentle, fear-free methods, we can help our pets feel more comfortable and confident, reducing the likelihood of problematic behaviors that may stem from underlying emotional distress. This holistic approach to training and behavior modification can create more effective and humane outcomes for our animal companions.
By considering the emotional lives of our pets and integrating this understanding into our training and behavior management practices, we can foster a deeper connection with our furry, feathered, or scaly friends, and provide them with the care and support they truly need to thrive.
Animal-Assisted Therapy and Emotional Support
Animals can serve as powerful sources of comfort and emotional support for humans. Therapy dogs, for instance, are often brought into hospitals or nursing homes to help reduce patients’ stress and anxiety. Researchers have found that the focused attention and calming presence of these animals can have therapeutic benefits, tapping into the innate abilities of pets to provide emotional support.
Therapeutic Benefits of Human-Animal Interactions
The interaction between humans and animals, whether in formal therapy settings or casual daily encounters, can have profound emotional and psychological benefits. Petting a dog or cat has been shown to lower blood pressure, reduce anxiety, and promote the release of feel-good hormones like oxytocin, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression and loneliness. This powerful connection between humans and animals highlights the important role that pets and human-animal bond can play in supporting emotional intelligence in animals and understanding pet emotions.
Pets as Emotional Companions
Beyond formal therapy settings, pets can also act as emotional companions in our daily lives, offering a sense of purpose, reducing loneliness, and boosting overall well-being through the deep bonds we form with them. The neuroethology of companion animals suggests that the evolutionary basis of pet emotions has helped shape the unique emotional connections we share with our furry, feathered, and scaly friends. By decoding pet body language and reading pet body language, we can better understand how pets communicate their emotional intelligence and interspecies emotional communication, strengthening the animal-human bond and promoting pet mental health.

Cross-Species Emotional Communication
The ability to communicate emotions across species is a remarkable feat of evolution. By studying the ways in which animals, including pets, express and interpret emotional cues, researchers are gaining invaluable insights into the evolution of emotional intelligence. From decoding subtle body language and vocalizations to understanding the shared emotional foundations between humans and other species, this field of research sheds light on the complex and often surprising ways in which we can connect with the emotional lives of our animal companions.
Decoding Interspecies Emotional Signals
As I delve deeper into the science of pet emotions, I’m continually amazed by the diverse ways in which animals communicate their feelings. Whether it’s a dog’s tail wag, a cat’s purr, or a horse’s neigh, each species has developed unique methods of expressing a wide range of emotions, from joy and affection to fear and distress. By closely observing these behavioral and vocal cues, researchers are unlocking the secrets of interspecies emotional communication, allowing us to better understand and empathize with the inner experiences of our furry, feathered, and scaly companions.
The Evolution of Emotional Intelligence
Underpinning this remarkable ability to communicate emotions across species is the evolutionary journey that has shaped the emotional capacities of animals over millions of years. From the primal survival instincts of our earliest ancestors to the complex social and cognitive abilities of modern mammals and birds, the development of emotional intelligence has been closely tied to the unique challenges and adaptations faced by each species. By exploring this evolutionary perspective, scientists are shedding light on the shared emotional foundations that unite us with the animal kingdom, fostering a deeper appreciation for the diversity of emotional experiences in the natural world.

As I continue to unravel the mysteries of cross-species emotional communication, I am left in awe of the profound connections we can forge with the animals in our lives. By decoding their emotional signals and understanding the evolutionary basis of their feelings, we unlock new pathways to empathy, understanding, and a richer, more fulfilling relationship with the diverse inhabitants of our shared planet.
Ethical Considerations in Studying Pet Emotions
As the scientific study of pet emotions continues to advance, researchers must navigate a delicate balance between ensuring the welfare of the animals involved in their studies and maintaining scientific objectivity. Measures must be taken to minimize any potential stress or harm to the animals, and the research must be conducted in an ethical and transparent manner. At the same time, scientists must be mindful of the risk of anthropomorphism, or the tendency to attribute human-like emotions and behaviors to animals, and strive to interpret their findings with rigorous, evidence-based approaches that respect the inherent differences between species.
Ensuring Animal Welfare in Research
Conducting research on the emotional intelligence in animals requires a deep commitment to the well-being of the participants. Researchers must prioritize the animals’ physical and psychological needs, implementing protocols that minimize any distress or discomfort. This may involve using non-invasive observation methods, providing enrichment activities, and ensuring the animals have access to comfortable living environments. By upholding the highest standards of animal psychology and pet behavior analysis, scientists can gather valuable insights while preserving the pet mental health and animal-human bond.
Anthropomorphism and Scientific Objectivity
As researchers delve into the science of pet emotions and understanding pet emotions, they must be vigilant against the temptation to read pet body language and decode pet expressions through a human-centric lens. While interspecies emotional communication and neuroethology of companion animals can reveal remarkable similarities, it is crucial to avoid anthropomorphising the animals’ experiences. By maintaining a decoding pet body language and interspecies communication, scientists can ensure their findings are grounded in robust, objective analysis that respects the evolutionary basis of pet emotions and the inherent diversity of emotional capacities across the animal kingdom.
The Future of Pet Emotion Research
As the field of pet emotion research continues to evolve, scientists are exploring new technologies and methods to further our understanding of the emotional lives of our animal companions. From advanced brain imaging techniques to innovative behavioral studies, the future of this field promises to uncover even more insights into the complex emotional experiences of pets.
Emerging Technologies and Methods
Researchers are leveraging the rapid advancements in neuroscience, physiology, and data analytics to develop more sophisticated tools for studying pet emotions. Techniques like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) are allowing scientists to peer deeper into the brains of animals, revealing the neural correlates of emotional processing. Additionally, the use of machine learning and computer vision is enabling the development of automated systems that can accurately decode pet body language and vocalizations, providing new avenues for deciphering interspecies emotional communication.
Implications for Pet Care and Management
These breakthroughs in pet emotion research will have far-reaching implications for how we approach pet care and management. By gaining a more nuanced understanding of the emotional needs and experiences of our animal companions, we can design more tailored enrichment programs, training methods, and veterinary care protocols that prioritize their well-being. This knowledge will empower pet owners, animal behaviorists, and veterinary professionals to create environments and interactions that foster positive emotional states, reduce stress and anxiety, and strengthen the human-animal bond.
As the field of pet emotion research continues to evolve, we are on the cusp of a new era of understanding and appreciation for the emotional capacities of our animal friends. By embracing these advancements, we can forge deeper, more fulfilling connections with the pets that enrich our lives, and work towards a future where the emotional well-being of all creatures is prioritized and protected.
Conclusion
The emotional lives of our pets are rich, complex, and deeply intertwined with our own. By delving into the science of pet emotions, we are challenging long-held misconceptions and gaining a greater appreciation for the inner experiences of the animals we share our lives with. From decoding their body language and vocalizations to understanding the evolutionary foundations of their feelings, this field of research is revolutionizing how we approach pet care and the human-animal bond.
As we continue to explore the emotional world of our furry, feathered, and scaly companions, we unlock new opportunities to nurture their well-being, strengthen our connections, and foster a deeper respect for the diverse emotional capacities present throughout the natural world. The neuroethology of companion animals and our understanding of interspecies emotional communication have come a long way, and the future holds even more insights that can help us better understand and support the mental health of our pets.
By embracing the emotional intelligence in animals and reading pet body language to decode their expressions, we can build stronger animal-human bonds and provide the best possible care for our beloved pets and their emotional needs. The journey of understanding pet emotions is an ongoing one, but the rewards of this exploration are immeasurable, as we deepen our connection with the diverse and fascinating emotional lives of the creatures we share our world with.
FAQ
What do recent brain studies on dogs reveal about their emotional range?
How can physiological markers provide insights into the emotional states of animals?
How are pets able to communicate their emotions through body language and behavior cues?
What are some of the ways that pets can form deep emotional bonds and attachments, similar to humans?
How can understanding a pet’s emotional triggers and fears lead to improved behavior and a more positive emotional state?
How can the study of interspecies emotional communication shed light on the evolution of emotional intelligence?
What are some of the ethical considerations researchers must navigate in the study of pet emotions?
Source Links
- https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2018/02/power-pets
- https://www.snexplores.org/article/animal-emotion-behavior-welfare-feelings
- https://ivspet.com/blogs/international-veterinary-science/understanding-the-emotional-lives-of-our-pets

